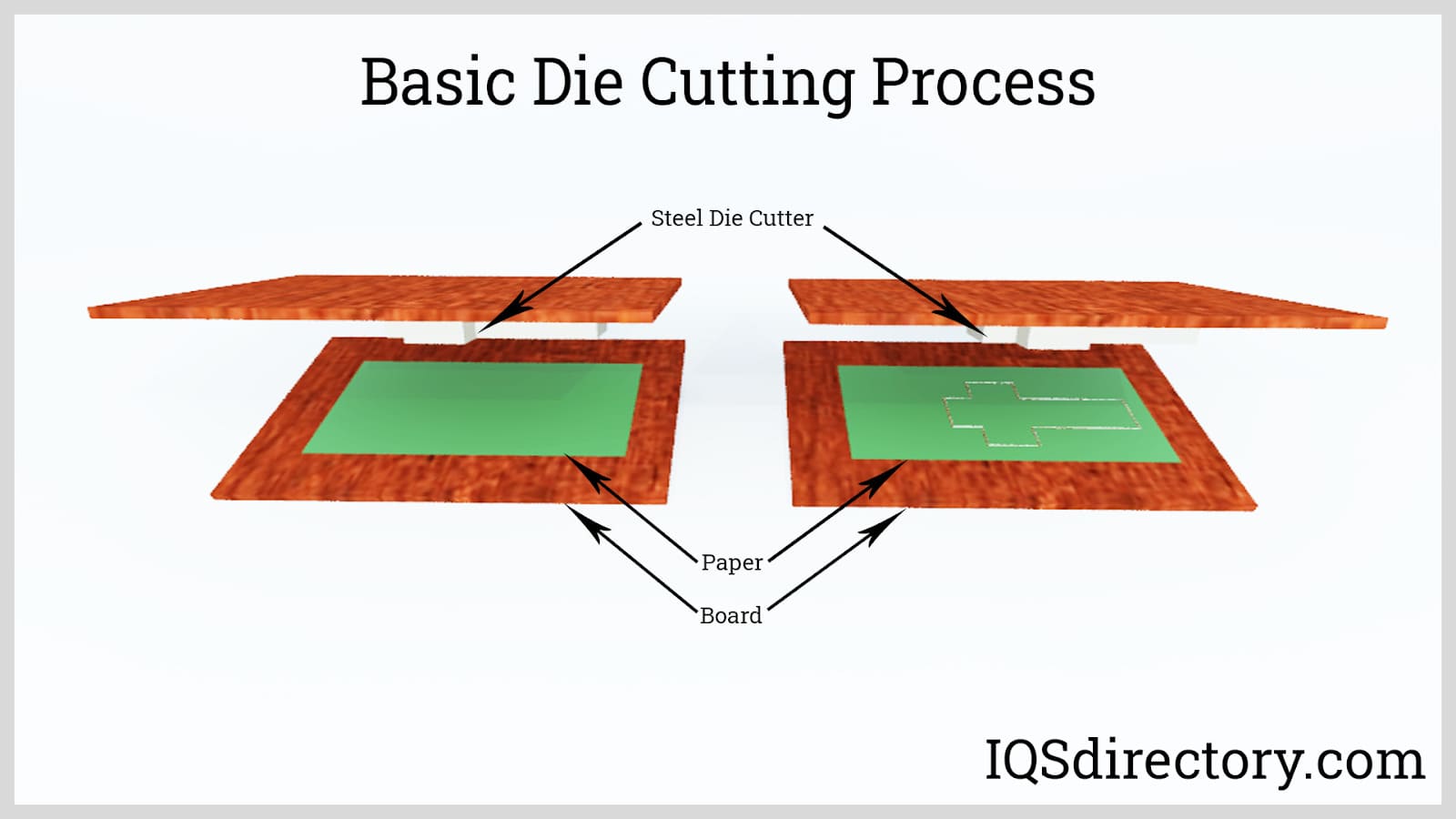
Die cutting is the manufacturing process of stamping or cutting two dimensional parts out of flat sheets of materials like rubber, fiber, paper, or metals. This process, often used in conjunction with laminating services, is a crucial finishing service for a wide range of parts and products.
We know that high tech products require die cut parts that are created with precision and care. We have the highest quality standards in the die cutting industry because we know that with die cutting accuracy is so important. After we cut the prototype for your product and after receiving your approval we pledge that your orders will be shipped within ten business days or less.
CFS produces industrial masking products and flexible, converted materials such as gaskets, spacers, thermal pads, and EMI shielding for finishers, OEMs, and related suppliers. Please visit customfabricate.com to request information or to browse our selection of products online.
When it comes to die cutting, we are the experts! We are a Grand Rapids, Michigan based company but we offer our services to all across the United States. It is our goal to bring exceptional die cutting services to all of our clients while also providing customer service that will keep you coming back to fulfill all of your die cutting needs. Our staff has the experience you can count on to...
National Rubber Corporation is a nationwide leader of die cutting services for a wide variety of industries and applications. We provide die cut product quantities from prototypes and short runs to large production runs. At National Rubber, we take pride in our ability to produce accurate die cut parts that are guaranteed to meet customer specifications and perform perfectly within the intended...

Gardico has been providing superior products and workmanship to industrial customers since 1977. Our die cutting capabilities satisfy needs for standard and custom gaskets, pads, insulators and decorative pieces in quantities from 5 or 10 to tens of thousands.

REDCO offers complete die cutting services to produce custom die cut gaskets and other custom die cuts that perfectly match our customers’ specifications. All of our steel rule dies are laser cut to guarantee quality and accuracy of the finished product. We have over 70 years of experience in die cutting non-metallic and metal parts. We strive to provide the best possible prices, the...
More Die Cutting Companies
Die cutting is a specialized fabrication process that stamps, cuts, or shapes two-dimensional parts from flat sheets of materials such as rubber, fiber, paper, plastics, foam, or metals. Frequently integrated with services like laminating, adhesive application, or finishing, die cutting is a foundational step in the production of a vast array of components for diverse industries. While the term “die cutting” can sometimes cause confusion due to its use in various fields, it typically refers to a process that goes beyond mere cutting. Dies not only shear materials but can also form or emboss shapes through compression and other mechanical stresses to achieve precise, repeatable end products.
Understanding the Die Cutting Process
The die cutting process is highly valued for its accuracy, repeatability, and versatility, making it indispensable for manufacturers requiring consistent shapes and dimensions. The first step begins with the design phase, where engineers or designers create detailed drawings or CAD models of the desired part or pattern. This design is then used to fabricate the die—a robust tool typically constructed from hardened steel, sometimes embedded with sharp blades or custom-shaped edges.
Once the die is ready, the target material—be it paper, felt, foam, cork, plastic, rubber, woven fabrics, adhesive tapes, or thin sheet metals—is prepared for processing. Material can be supplied in continuous rolls (web form) or as individual sheets or panels. The die cutting machine, which may be manual, semi-automatic, or fully automated, positions the material for precise engagement with the die. Applying controlled pressure, the machine drives the die through the material, creating clean, accurate cuts that match the original design. The result is a highly uniform batch of parts, ready for downstream use.
After cutting, the finished pieces are separated from the excess material, referred to as the “web” or “skeleton.” This waste is efficiently removed through manual or automated stripping, leaving only the desired die-cut shapes. The high speed and scalability of die cutting allow manufacturers to produce thousands—or even millions—of identical parts quickly, making it ideal for both high-volume production and prototyping.
Quality control is a critical component of the die cutting process. Inspections at various stages verify that each part meets stringent dimensional and visual standards. Any defective or out-of-spec parts are removed, ensuring reliable, high-quality outcomes for applications where performance and consistency are non-negotiable, such as in the automotive, electronics, or medical device industries.
After the initial die cutting, many parts undergo additional operations tailored to their intended application. In packaging, die-cut blanks may be folded, glued, or printed to form finished boxes or display cartons. Textile die cuts proceed to sewing or assembly lines for garment or accessory production. In electronics, die-cut insulators or gaskets are layered with adhesives or assembled into multi-component modules. This flexibility makes die cutting an integral part of complex manufacturing workflows.
Different Types of Die Cutting Methods
Die cutting is not a one-size-fits-all process. Various methods and machines are employed based on factors such as material type, thickness, production volume, and complexity of the desired shape. Understanding these techniques helps businesses select the optimal solution for their application.
Flatbed Die Cutting
Flatbed die cutting is perhaps the most widely used technique in the converting and fabrication industry. Utilizing a flatbed press, this method employs a stationary die to stamp shapes from flat sheets or webs with high precision. Its adaptability allows for quick changeovers and the processing of a broad range of materials, including paperboard, corrugated cardboard, plastics, and some metals.
Common applications include the production of labels, business cards, folding cartons, gaskets, and other packaging materials. The flatbed method excels at delivering sharp, accurate cuts and can accommodate both small and large production runs. Its straightforward tooling and setup make it a popular choice for custom die cutting jobs, prototypes, and short-run manufacturing.
Rotary Die Cutting
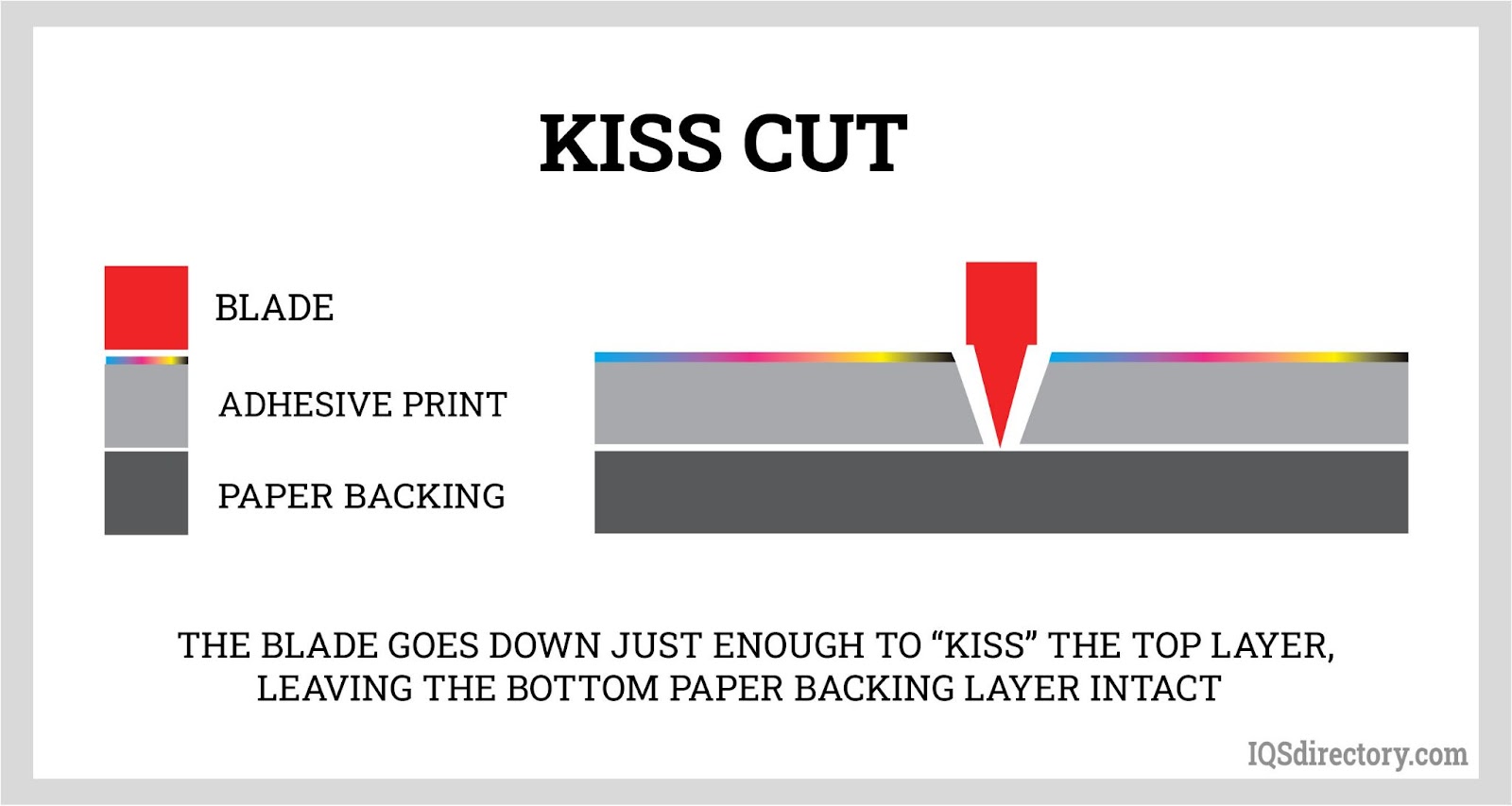
Rotary die cutting leverages a cylindrical die that continuously cuts shapes from material fed in web or roll form. This setup enables rapid, high-volume production—making it the method of choice for long runs of labels, adhesive tapes, stickers, medical components, and membrane switches. Rotary systems can incorporate additional features such as kiss cutting (partially cutting through layers), perforating, or laminating in a single pass, further enhancing efficiency. The continuous nature of rotary die cutting ensures minimal downtime and maximized throughput, which is especially beneficial for industries demanding speed and consistency.
Steel Rule Die Cutting
Steel rule die cutting involves embedding sharp steel blades (rules) into a wooden or composite base to form a custom die for cutting soft, compressible materials. This versatile and cost-effective approach is ideal for foam inserts, gaskets, nonwovens, textiles, and packaging foams. Its flexibility allows for intricate designs and rapid prototyping, while its reusability ensures cost savings on repeat orders. Steel rule dies can be crafted quickly, making them suitable for both small-batch and moderate production volumes.
Laser Die Cutting
Laser die cutting uses high-powered lasers to precisely cut, etch, or perforate materials without the need for physical dies. This digital process is perfect for intricate, complex, or variable designs and offers unmatched flexibility—design changes can be implemented instantly without fabricating new dies. Laser die cutting is especially beneficial for prototypes, low-volume production, and projects requiring detailed graphics or fine tolerances. Materials commonly processed include films, plastics, rubber, thin metals, adhesives, and specialty papers. The non-contact nature of laser cutting also eliminates tool wear, ensuring consistent results.
Waterjet Die Cutting
Waterjet die cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water—sometimes mixed with abrasive particles—to cut through tough or heat-sensitive materials. This process is ideal for composites, foams, rubber, textiles, and even certain metals that might be damaged or distorted by traditional die cutting or laser processes. Waterjet cutting produces smooth edges without introducing thermal stress, making it a preferred choice for applications where material integrity and edge quality are critical, such as aerospace, automotive, and custom gasket manufacturing.
When selecting a die cutting method, consider the material’s properties (thickness, hardness, compressibility), the complexity of the design, required tolerances, production volume, and budget. For example, rotary die cutting is optimal for high-volume runs of labels, while laser die cutting suits low-volume, intricate custom work. In some cases, hybrid solutions—combining two or more cutting technologies—deliver the best results, allowing manufacturers to balance cost, speed, and precision.
History and Evolution of Die Cutting Technology
The origins of die cutting can be traced to the mid-19th century, where it revolutionized the shoe industry by automating the tedious process of hand-cutting leather. Early die cutting presses enabled workers to stamp uniform leather pieces for footwear, vastly improving productivity and consistency.
By the early 1900s, advances like the swing arm clicker press allowed for simultaneous cutting of multiple shapes and sizes, paving the way for the mass production of not just shoes but also industrial parts such as gaskets, tubing, and packaging materials. The post-war manufacturing boom of the 1950s saw engineers shrink die cutting machines into compact, portable units, further democratizing access to precision cutting technology for small businesses, schools, and crafters.
The digital age ushered in a new era for die cutting. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and automated die cutting systems have enabled the production of highly intricate shapes and rapid prototyping. Today, advanced robotics, high-pressure presses, and laser or waterjet cutters can process everything from delicate films to hardened metals. Consumer-level innovations—such as the Cricut Expression and Silhouette Cameo—have brought die cutting to home crafters and educators, making custom cutting accessible at the touch of a button.
The evolution of die cutting technology continues, with the integration of IoT-enabled machines, real-time quality monitoring, and cloud-based design sharing, opening new frontiers for efficiency, customization, and collaboration in both industrial and creative sectors.
Limitations and Considerations in Die Cutting
While die cutting is a powerful and efficient manufacturing process, it does have limitations. Traditional die cutting struggles with highly intricate or detailed designs, especially in thick, dense, or brittle materials where maintaining fine tolerances is challenging. Even with advanced laser die cutting, not all materials or production volumes are suitable, and the process can become costly for complex designs or short runs.
Material selection is crucial; flat, uniformly thick substrates yield the best results, while excessively thick or rigid materials can damage dies or require prohibitively high pressures. Fragile or brittle materials may crack or shatter during cutting. The initial investment in custom tooling can be significant—making die cutting less cost-effective for one-off or low-volume jobs.
Die cutting also generates material waste in the form of the web or skeleton. Manufacturers must optimize die layouts using nesting software to minimize offcuts and maximize yield. Any misalignment between the die and material can lead to defects that compromise product appearance or function. Additionally, there are thickness limitations—beyond a certain point, alternative fabrication methods such as CNC machining or waterjet cutting may be necessary.
Are you curious about which die cutting method is right for your material or project? Or do you need guidance optimizing material usage to reduce waste and cost? Contact a die cutting expert for a personalized consultation.
Modern Advancements in Die Cutting
Die cutting technology has advanced rapidly, driven by automation, digital design, and the demand for greater customization. CAD software allows engineers to design highly detailed dies, which are then manufactured with extreme precision. Automated die cutting machines equipped with vision systems and robotics ensure precise registration and consistent quality, reducing manual intervention and minimizing defects.
Manufacturers increasingly use multi-step die cutting for challenging materials or complex shapes. This involves multiple passes with varying pressure or depth settings, allowing thicker or layered materials to be cut cleanly without damaging the die or substrate.
Minimizing waste is a top priority. Advanced nesting algorithms arrange shapes on the material to maximize efficiency, reducing scrap and lowering production costs. Real-time quality monitoring and process analytics help identify and correct issues instantly, further improving yields.
Hybrid solutions—combining die cutting with laser, waterjet, or CNC machining—are expanding the range of materials and geometries that can be processed. These integrated systems allow for efficient handling of tough composites, multi-layer laminates, and highly intricate parts, making it possible to address applications once thought impossible for traditional die cutting.
Looking for ways to future-proof your manufacturing process with the latest die cutting technology? Explore advanced automation and hybrid solutions with our vetted supplier network.
Key Benefits and Advantages of Die Cutting
Die cutting offers a compelling combination of precision, repeatability, versatility, and efficiency, making it a go-to solution for mass production and custom fabrication across a spectrum of industries. Here are some of the primary advantages:
- High Precision and Uniformity: Specialized dies ensure consistent, repeatable shapes and dimensions, critical for industries like electronics, automotive, and medical devices where even minor deviations can impact function or assembly.
- Scalability and Speed: Die cutting is exceptionally fast, capable of producing thousands of identical parts per hour with minimal manual intervention, maximizing throughput and lowering labor costs.
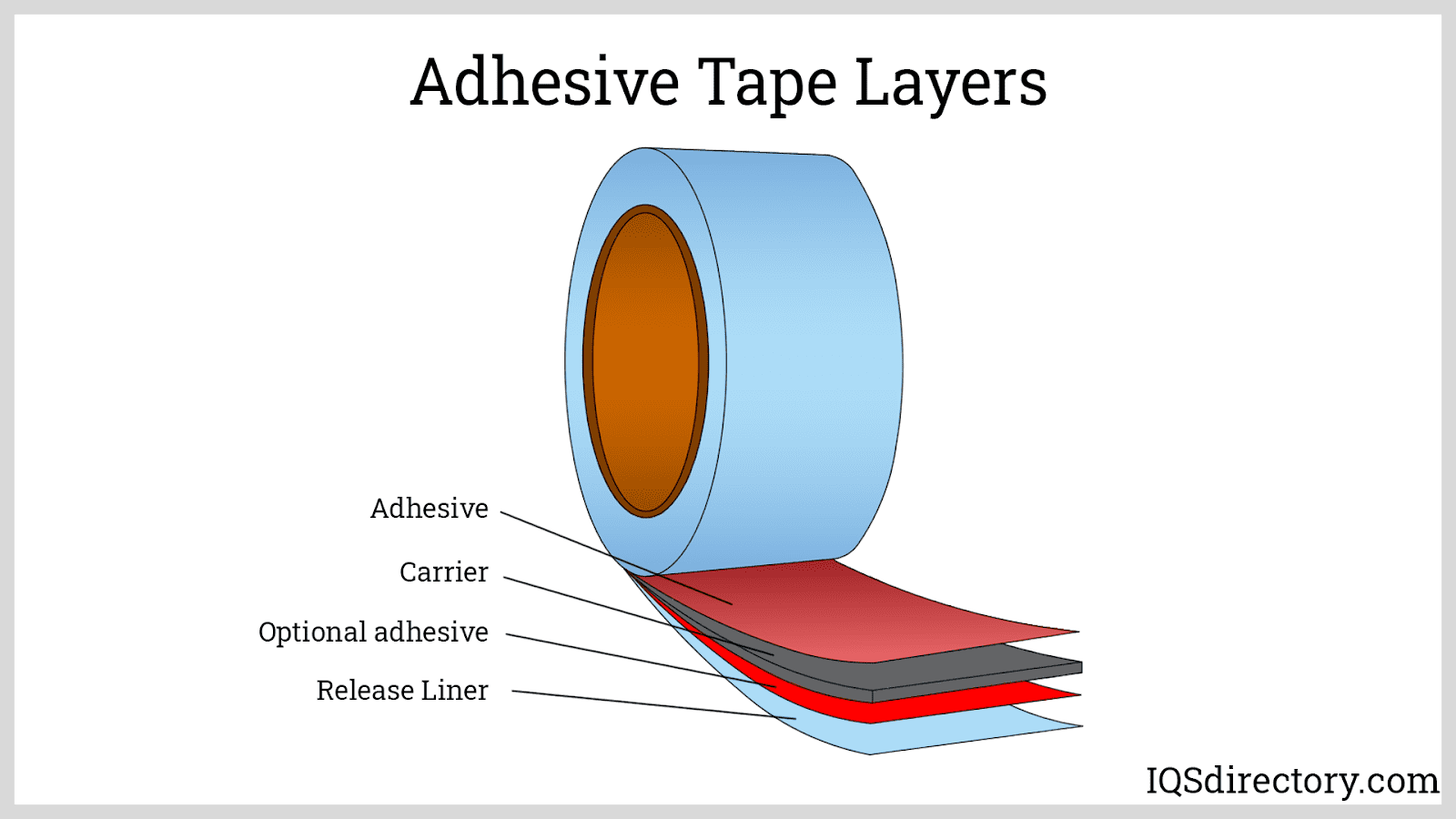
- Versatility Across Materials: From paper and textiles to plastics, foams, adhesives, and thin metals, die cutting accommodates an impressive array of substrates. This flexibility allows manufacturers to address diverse application needs with a single process.
- Intricate and Complex Designs: Modern die cutting—especially when paired with laser or digital control—can achieve detailed patterns, perforations, and custom shapes not easily replicated by other methods.
- Clean, Smooth Edges: Die cut products typically feature crisp, clean edges, enhancing both their visual appeal and functional performance—an essential attribute in packaging, medical, and consumer products.
- Cost-Effective for High Volume: Once the die is created, per-part production costs drop dramatically, making die cutting an economical choice for medium-to-large production runs compared to labor-intensive alternatives.
- Consistent Quality and Low Waste: Automated quality control, optimized nesting, and efficient material usage ensure high yields and minimal scrap, supporting sustainability and cost savings.
Compared to other fabrication techniques—such as laser cutting, waterjet cutting, CNC routing, or manual cutting—die cutting stands out for speed, cost-efficiency, and the sheer variety of materials it can process. While some alternatives may be better suited to ultra-thick or highly detailed components, die cutting remains the preferred option for mass production, packaging, and custom part manufacturing.
Not sure if die cutting is the right fit for your project? Get a free consultation and discover how die cutting can streamline your production, reduce costs, and deliver unmatched quality.
Applications and Industry Use Cases for Die Cutting
Die cutting is a cornerstone process in modern manufacturing, touching nearly every industry. Its adaptability makes it indispensable for both standard and highly specialized applications. Below are just a few of the many sectors where die cutting plays a vital role:
- Printing and Packaging: Die cutting transforms flat materials like paperboard and corrugated fiberboard into business cards, brochures, folders, blister packs, folding cartons, and custom packaging. Precision cutting and scoring enable unique branding and product protection solutions.
- Textiles and Apparel: Fabrics are die cut into garment pieces, appliques, patches, and home furnishings, ensuring accuracy, repeatability, and minimal waste. This streamlines sewing, assembly, and finishing processes.
- Automotive: Gaskets, seals, insulation pads, and interior trim components are die cut from rubber, foam, felt, and composite materials. These precision parts are essential for vehicle safety, comfort, and reliability.
- Electronics: Die cut insulators, thermal pads, adhesive tapes, EMI/RFI shielding, and protective films are critical for device assembly, electrical isolation, and thermal management in electronics manufacturing.
- Medical Devices and Diagnostics: Die cutting is used to manufacture wound dressings, surgical masks, diagnostic test strips, electrode pads, and custom medical components, meeting stringent hygiene and quality standards.
- Aerospace and Defense: Specialized die cut components such as thermal and acoustic insulators, gaskets, and sealing solutions are vital for aircraft, spacecraft, and defense equipment, where performance and safety are paramount.
- Crafting, Stationery, and Creative Arts: Home crafters and commercial printers use die cutting to create greeting cards, invitations, stickers, stencils, scrapbooking elements, and intricate decorative items. Desktop die cutting machines empower DIY enthusiasts to produce custom designs with ease.
- Industrial Manufacturing: In sectors like appliance manufacturing, HVAC, and construction, die cut parts—ranging from rubber feet and vibration dampers to filters and shielding—support efficient assembly and reliable product performance.
Are you searching for industry-specific die cutting solutions for your business? Browse our directory or request a quote from leading die cutting companies with expertise in your sector.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Die Cutting Manufacturer
Selecting the right die cutting partner is a crucial decision that directly impacts product quality, cost, and lead time. Here’s what to consider when evaluating die cutting service providers:
- Technical Expertise and Capabilities: Does the manufacturer have experience with your material, application, and required tolerances? Can they offer value-added services like laminating, adhesive application, or kitting?
- Production Capacity: Assess whether the company can handle your order volume—whether it’s rapid prototyping, small-batch runs, or large-scale production.
- Quality Assurance: Look for ISO certifications, documented quality control processes, and a track record of consistent, defect-free production.
- Lead Time and Flexibility: Can the provider accommodate tight deadlines or design changes? Do they offer expedited services or flexible order quantities?
- Cost Structure: Evaluate tooling costs, per-part pricing, material markups, and shipping options. Some providers offer volume discounts or value engineering support to optimize costs.
- Customer Support and Communication: Responsive communication, technical guidance, and transparent project management are key to a successful partnership.
For the best results, leverage our comprehensive directory to compare multiple die cutting companies. Each listing features a detailed profile outlining capabilities, specialties, certifications, and customer reviews. Our patented website previewer lets you quickly assess each company’s strengths, while our streamlined RFQ (Request for Quote) form enables you to contact several manufacturers simultaneously—saving time and ensuring you find the perfect match for your project.
Ready to get started? Browse our die cutting company listings or request a quote to connect with industry-leading die cutting suppliers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Die Cutting
What materials can be die cut?
Die cutting is compatible with a wide range of materials, including paper, cardboard, plastics, foams, rubber, textiles, nonwovens, adhesives, thin metals, and laminates. Selecting the right method and die ensures optimal results for your chosen substrate.
How do I select the best die cutting method for my application?
Consider factors such as material type, thickness, desired shape complexity, production volume, and required tolerances. Flatbed die cutting is versatile for general applications, rotary die cutting excels at long runs of web materials, and laser or waterjet cutting is ideal for intricate or specialty projects.
Is die cutting suitable for custom shapes and short production runs?
Yes—while traditional die cutting is most cost-effective for high-volume production, digital and laser die cutting offer flexibility and fast turnaround for custom or low-quantity jobs without the need for physical tooling.
What industries benefit most from die cutting?
Industries including packaging, electronics, automotive, medical devices, aerospace, textiles, and creative arts all rely heavily on die cutting for their manufacturing and assembly operations.
How can I get a quote for die cutting services?
Use our die cutting company directory to find and contact multiple suppliers, or fill out our easy RFQ form to receive competitive quotes tailored to your project requirements.
Still have questions about die cutting or need help choosing a provider? Connect with our experts for personalized advice and recommendations.
Get Started With the Right Die Cutting Partner
Your choice of die cutting partner can make all the difference in product quality, cost, and speed to market. By exploring our directory, comparing manufacturer profiles, and leveraging our RFQ tools, you can quickly identify the best match for your needs—whether you require simple packaging, complex medical components, or custom gaskets for industrial machinery.
Take the next step: Discover more die cutting companies or request a quote today and streamline your path to efficient, high-quality manufacturing.
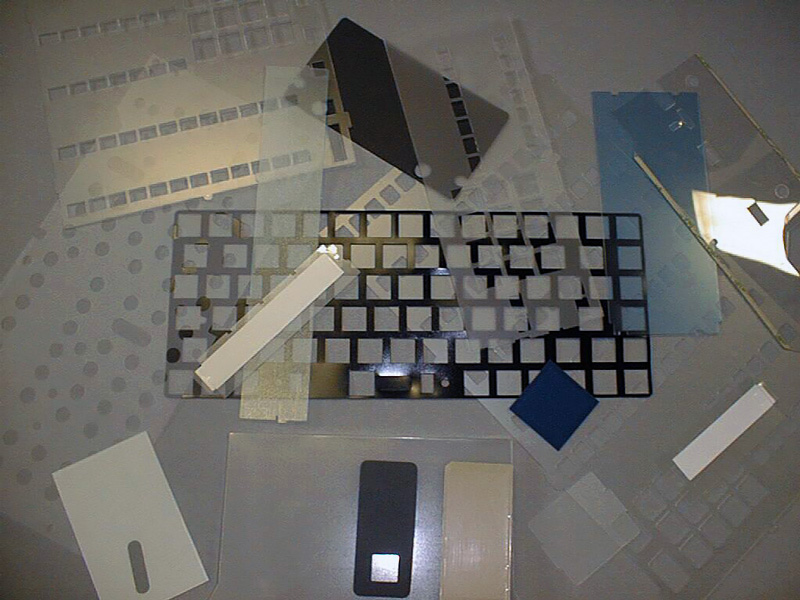


 Die Cutting
Die Cutting Foam Fab
Foam Fab Gaskets
Gaskets O-rings
O-rings Plastic Fabricators
Plastic Fabricators Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services